Apache 讲解
概述
简单服务器流程
Q1:简述在浏览器中输入 www.baidu.com 之后发生的一系列事情
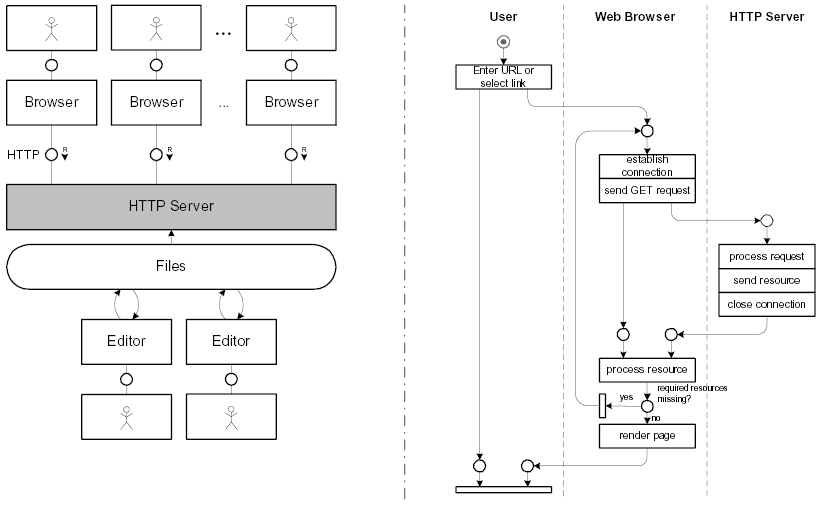
appendix1:http1.0 vs http1.1
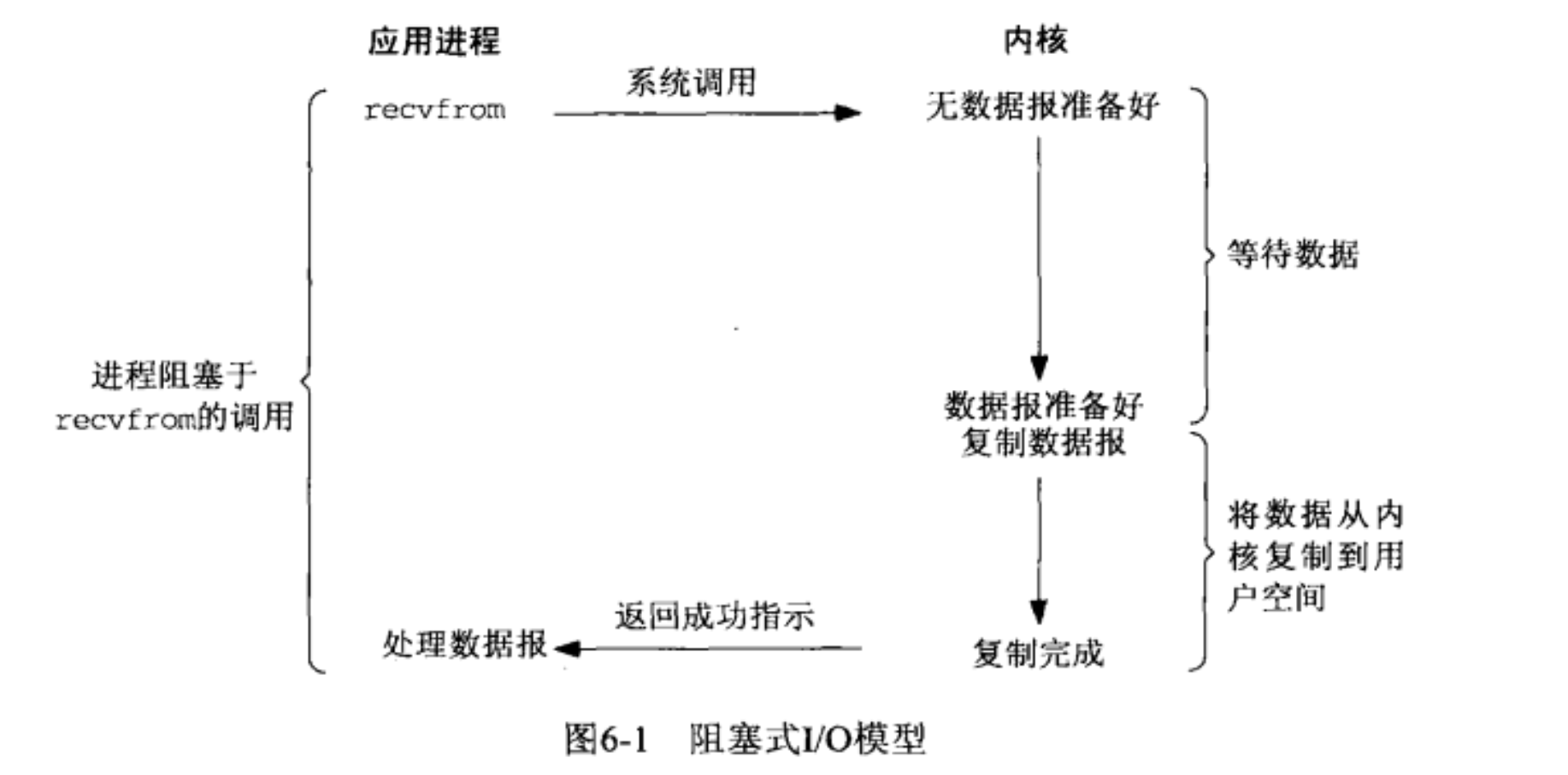
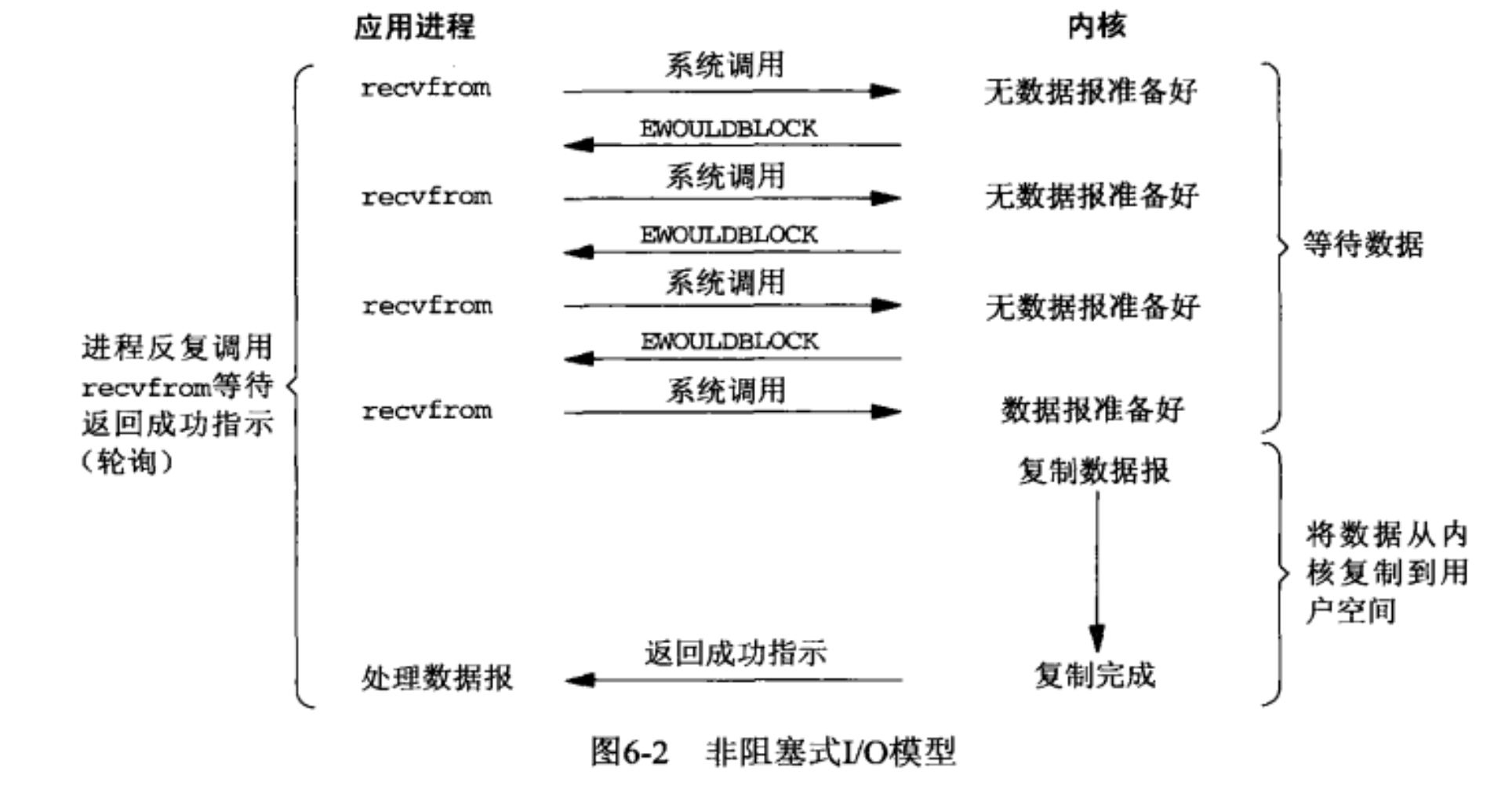
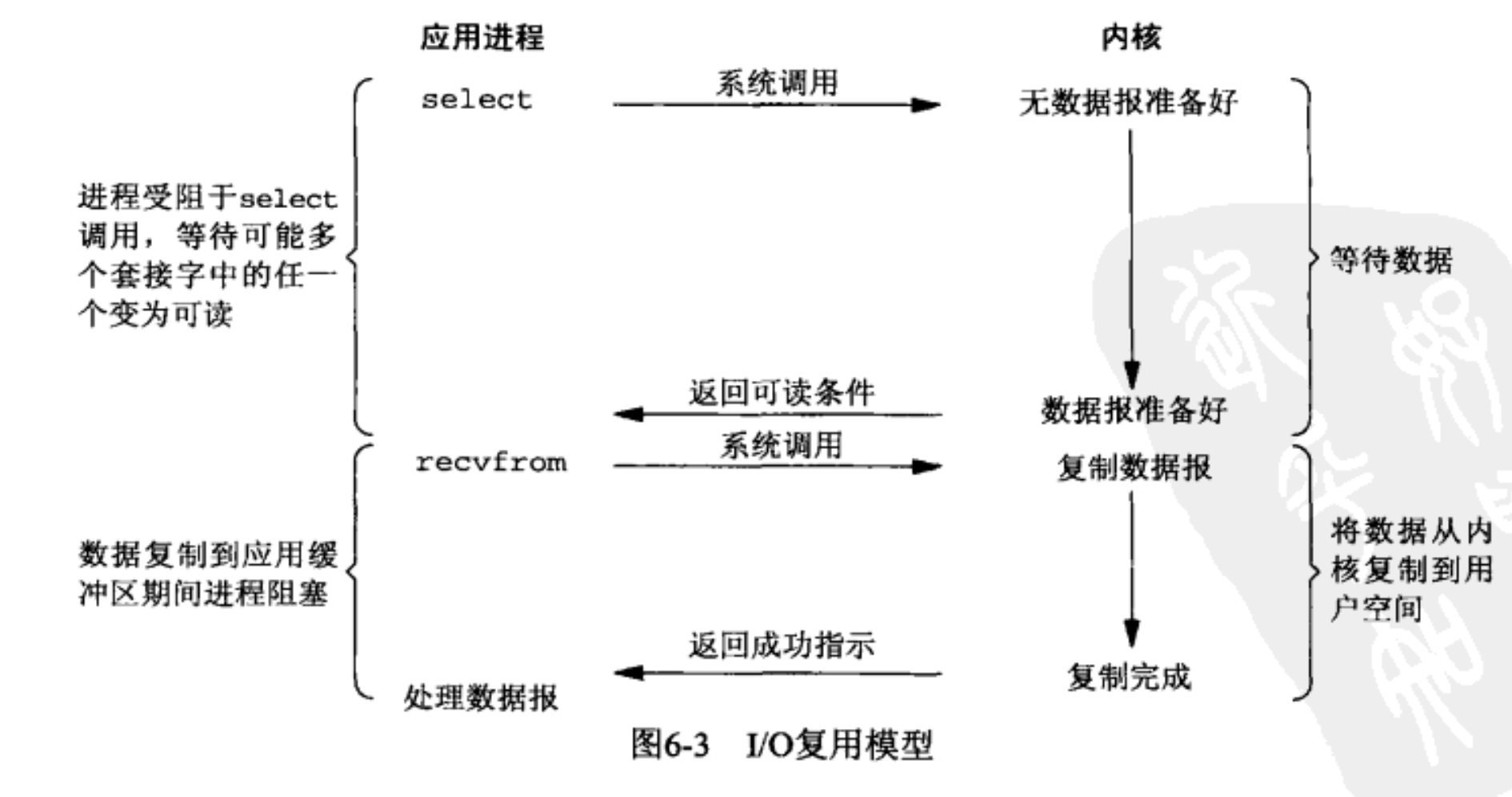
I/O 模型
- 阻塞式 I/O 模型
- 非阻塞 I/O 模型
- I/O 复用 模型
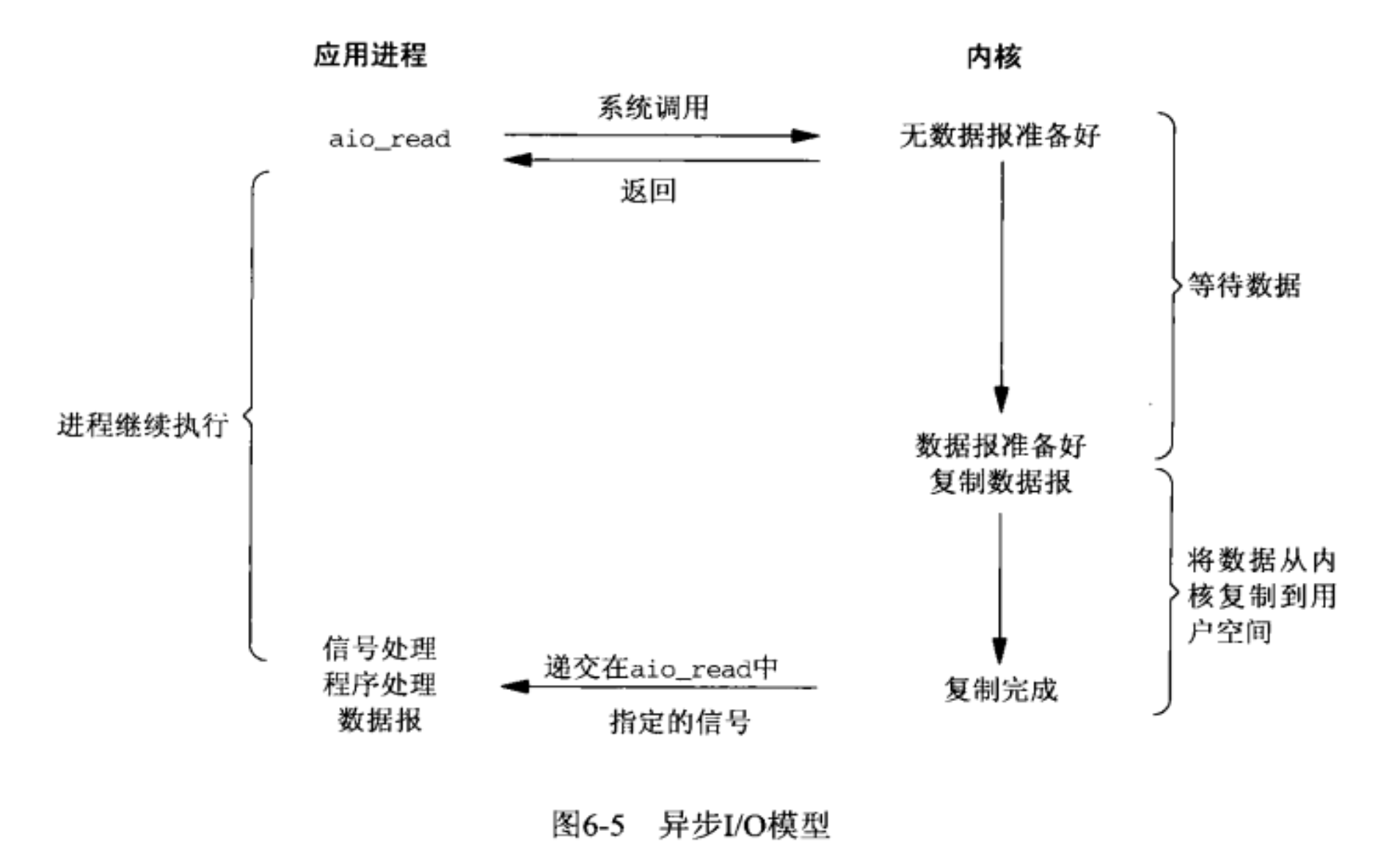
- 异步 I/O 模型
工作模式
查看apache的工作模式
/usr/sbin/apachectl -V
内存管理
核心数据结构
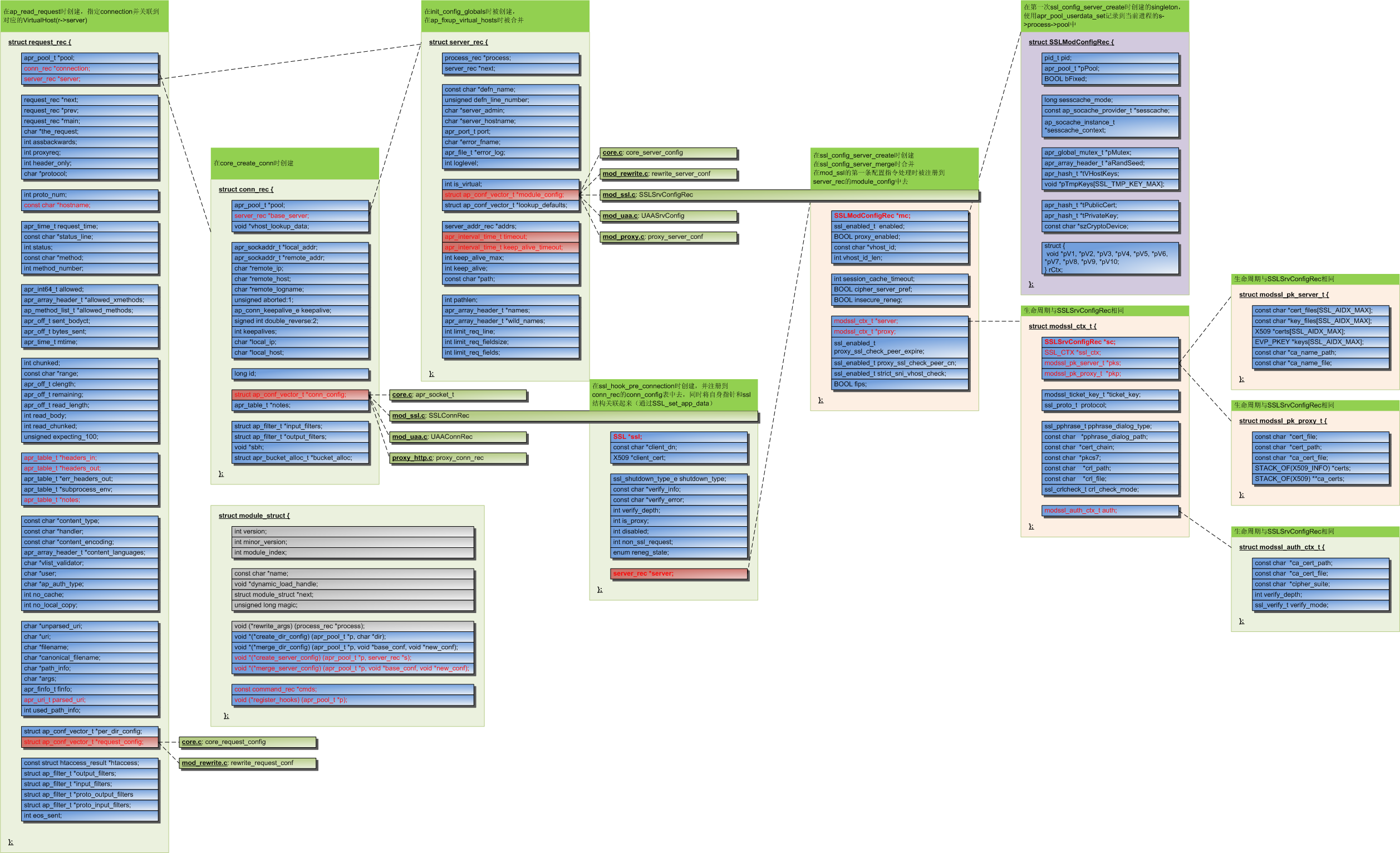
request的关键元素
The most essential part of any request is the request record. In a call to a handler function, this is represented by the request_rec structure passed along with every call that is made. This struct, typically just referred to as r in modules, contains all the information you need for your module to fully process any HTTP request and respond accordingly.
Some key elements of the request\_recstructure are:
r->handler (char*):Contains the name of the handler the server is currently asking to do the handling of this requestr->method (char*):Contains the HTTP method being used, f.x. GET or POSTr->filename (char*):Contains the translated filename the client is requestingr->args (char*):Contains the query string of the request, if anyr->headers_in (apr_table_t*):Contains all the headers sent by the clientr->connection (conn_rec*):A record containing information about the current connectionr->user (char*):If the URI requires authentication, this is set to the username providedr->useragent_ip (char*):The IP address of the client connecting to usr->pool (apr_pool_t*): The memory pool of this request. We’ll discuss this in the “Memory management” chapter.
mod_helloworld 模块讲解
apxs -n helloworld -g
Defining a module
#include "httpd.h"
#include "http_config.h"
#include "http_protocol.h"
#include "ap_config.h"
/* The sample content handler */
static int helloworld_handler(request_rec *r)
{
if (strcmp(r->handler, "helloworld")) {
return DECLINED;
}
r->content_type = "text/html";
if (!r->header_only)
ap_rputs("The sample page from mod_helloworld.c\n", r);
return OK;
}
static void helloworld_register_hooks(apr_pool_t *p)
{
ap_hook_handler(helloworld_handler, NULL, NULL, APR_HOOK_MIDDLE);
}
/* Dispatch list for API hooks */
/* 标记服务器能够加载的模块名 */
/* 为模块配置设置一个命名空间 */
module AP_MODULE_DECLARE_DATA helloworld_module = {
STANDARD20_MODULE_STUFF,
NULL, /* create per-dir config structures */
NULL, /* merge per-dir config structures */
NULL, /* create per-server config structures */
NULL, /* merge per-server config structures */
helloworld_directives, /* table of config file commands */
helloworld_register_hooks /* register hooks */
};
指令
typedef struct {
int enabled; /* Enable or disable our module */
const char *path; /* Some path to...something */
int typeOfAction; /* 1 means action A, 2 means action B and so on */
} example_config;
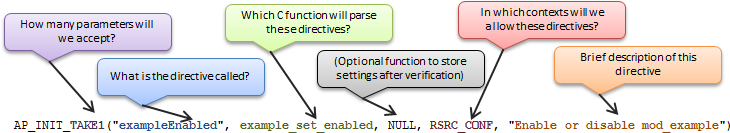
static const command_rec helloworld_directives[] =
{
AP_INIT_TAKE1("exampleEnabled", example_set_enabled, NULL, RSRC_CONF, "Enable or disable mod_example"),
AP_INIT_TAKE1("examplePath", example_set_path, NULL, RSRC_CONF, "The path to whatever"),
AP_INIT_TAKE2("exampleAction", example_set_action, NULL, RSRC_CONF, "Special action value!"),
{ NULL }
};
配置的作用域
- OR_ALL 所有的地方使用
- ACCESS_CONF:允许指令出现这Directiory Location 区间以内的顶级命令区,一般是用来设置特定文的指令控制
- RSRC_CONF: 允许指令出现在 Directiory Location 区间以外的顶级命令区
配置段合并
配置段会按非常特别的顺序依次生效,由于这会对配置指令的处理结果产生重大影响,因此理解它的流程非常重要。
合并的顺序是:
<Directory>(除了正则表达式)和.htaccess同时处理;(如果允许的话,.htaccess的设置会覆盖<Directory>的设置)<DirectoryMatch>(和<Directory ~>)<Files>和<FilesMatch>同时处理<Location>和<LocationMatch>同时处理
除了<Directory>,每个组都按它们在配置文件中出现的顺序被依次处理,而<Directory>(上面的第1组),会按字典顺序由短到长被依次处理。例如:<Directory /var/web/dir>会先于<Directory /var/web/dir/subdir>被处理。如果有多个指向同一个目录的<Directory>段,则按它们在配置文件中的顺序被依次处理。用Include指令包含进来的配置被视为按原样插入到Include指令的位置。
位于<VirtualHost>容器中的配置段在外部对应的段处理完毕*以后*再处理,这样就允许虚拟主机覆盖主服务器的设置。
代码示例
void *create_dir_conf(apr_pool_t *pool, char *context) {
context = context ? context : "(undefined context)";
example_config *cfg = apr_pcalloc(pool, sizeof(example_config));
if(cfg) {
/* Set some default values */
strcpy(cfg->context, context);
cfg->enabled = 0;
cfg->path = "/foo/bar";
cfg->typeOfAction = 0x11;
}
return cfg;
}
void *merge_dir_conf(apr_pool_t *pool, void *BASE, void *ADD) {
example_config *base = (example_config *) BASE ; /* This is what was set in the parent context */
example_config *add = (example_config *) ADD ; /* This is what is set in the new context */
example_config *conf = (example_config *) create_dir_conf(pool, "Merged configuration"); /* This will be the merged configuration */
/* Merge configurations */
conf->enabled = ( add->enabled == 0 ) ? base->enabled : add->enabled ;
conf->typeOfAction = add->typeOfAction ? add->typeOfAction : base->typeOfAction;
strcpy(conf->path, strlen(add->path) ? add->path : base->path);
return conf ;
}
module AP_MODULE_DECLARE_DATA example_module =
{
STANDARD20_MODULE_STUFF,
create_dir_conf, /* Per-directory configuration handler */
merge_dir_conf, /* Merge handler for per-directory configurations */
NULL, /* Per-server configuration handler */
NULL, /* Merge handler for per-server configurations */
directives, /* Any directives we may have for httpd */
register_hooks /* Our hook registering function */
};
hook 钩子
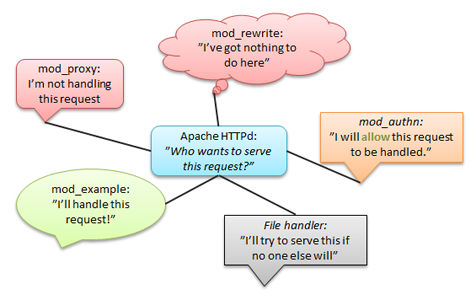
钩子的处理
/*在这个钩子处按照顺序运行所有的被注册函数*/ AP_IMPLEMENT_HOOK_VOID(do_something, (request_rec *r, int n), (r, n))/*在这个钩子处运行所有的被注册函数直到返回了一个不是DECLINED的值*/ AP_IMPLEMENT_HOOK_RUN_FIRST(int, do_something, (request_rec *r, int n), (r, n), DECLINED)/*运行所有的函数直到或者除非返回一个错误*/ AP_IMPLEMENT_HOOK_RUN_ALL(int, do_something, (request_rec *r, int n), (r, n), OK, DECLINED)
其它有用的钩子
Hooking into the request handling phase is but one of many hooks that you can create. Some other ways of hooking are:
ap_hook_child_init: Place a hook that executes when a child process is spawned (commonly used for initializing modules after the server has forked)ap_hook_pre_config: Place a hook that executes before any configuration data has been read (very early hook)ap_hook_post_config: Place a hook that executes after configuration has been parsed, but before the server has forkedap_hook_translate_name: Place a hook that executes when a URI needs to be translated into a filename on the server (thinkmod_rewrite)ap_hook_quick_handler: Similar toap_hook_handler, except it is run before any other request hooks (translation, auth, fixups etc)ap_hook_log_transaction: Place a hook that executes when the server is about to add a log entry of the current request